WGU C100 CH 6 NeoClassical Period
Essay,
Pages 20 (4873 words)
Views
101
Neoclassical themes
skepticism, rationalism, empiricism, logic, progress, revolution, order, clarity, deism, classicism
Neoclassic Context
Enlightenment, Declaration of independence
Neoclassical Religion
enlightenment, philosophies, deism
Neoclassic Philosophers
Voltaire – satire attacks – Optimism of Gottfried Leibniz, Denis Diderot – Encyclopedie, Thomas Hobbes – Levithan
Neoclassical Literature
Enlightenment, the novel, Jean-Jaques Rousseau – Emile, Samuel Richardson – pamela, Alexander pope – The rape of the lock
Neoclassical Theater
Myths, “The heroic tragedy” or “comedy of matters”, Jean Batiste Moliere – Tartuffe, Jean Racine, Pierre Corneille
Neoclassical Art and Architecture
Order progress and civic virtue Greek and Roman styles, Johann Joachim Wincklmann, Jacques-Louis David, Angelica Kaufmann, John Singleton Copley, Henry Fuseli, William Hunter.
Brandenburg gate, Pantheon in Paris and Monticello, Thomas Jefferson’s home in VA
Neoclassical music
Mozart – sonatas, symphonies, masses, concertos, operas, Haydn – Clock symphony, Beethoven no5 and no9
Neoclassical enlightenment influences
Jonathon swifts – gullivers tales – Political satire, Bernstein
The Age of Enlightenment was also called ________.
The Age of Reason
The music of the Neoclassical Period differed from Baroque music in that ________.
it featured more variety in orchestral texture and reflected the Enlightenment focus on balance, order, and structural clarity.
Which one of the following statements about Neoclassical theater is true?
Tragedy and comedy were not mixed. Neoclassical theater featured either “the heroic tragedy” or “the comedy of manners.”
The classical movement in music falls between which two periods for the Neoclassical/Enlightement period
The classical movement in music falls between the Baroque and Romantic Periods.
Which of the following composers was a classical composer?
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart was a classical composer.
Neoclassicism perpetuated the lavish, ornate aesthetic of the Baroque Period. True or False?
False, Neoclassicism rejected the ostentatious displays of Baroque works and embraced harmony and balance.
Of the following artists, who worked within the Neoclassical movement?
Angelica Kauffmann was one of the few prominent female Neoclassical artists.
Which of the following individuals was NOT an Enlightenment philosopher?
Leonardo Bruni was a Renaissance philosopher. John Locke, Immanuel Kant, and Denis Diderot were all Enlightenment philosophers.
Enlightenment thinking valued all of the following EXCEPT __________.
mysticism, Enlightenment thinking valued logic, order, and clarity. For Enlightenment philosophers, reason, rational thinking, and observation were key to uncovering philosophical truths.
The Age of Enlightenment is also known as the Age of Expansion. True or False?
False, the Age of Enlightenment is also known as the Age of Reason.
Who said, “The age we live in is a busy age, in which knowledge is rapidly advancing towards perfection”?
It was English philosopher Jeremy Bentham
What was the goal of the Encyclopédie?
The Encyclopédie was a project started by French writers and thinkers to collect human knowledge in one place.
What position would an Enlightenment philosopher take on the following quote by Saint Augustine? “Faith is to believe what you do not see; the reward of this faith is to see what you believe.”
They would probably disagree, Enlightenment thinkers believed in using reason and logic to deduce truths about the world. Trusting without evidence, as the quote suggets a person do, conflicts with those Enlightenment principles.
Some of the greatest political fiction was born of the Enlightenment principle that ruling authority is derived from the assent of the governed and not from the divine right of kings. Rulers like Catherine the Great and Joseph the II felt that their authority was threatened. True or false?
False, Some of the greatest political fiction was born of the Enlightenment principle that ruling authority is derived from the assent of the governed and not from the divine right of kings. Rulers like Catherine the Great and Joseph the II felt that their authority was threatened. True or false?
What is empiricism?
Empiricism, or the theory that all knowledge comes from the direct experience of the senses, is the foundation of the modern scientific method, in which observation and experimentation lead to ideas and theories.
Which of the following beliefs would a deist likely hold?
Death has a scientific explanation, the laws of which God created, Deists did believe in God as a creator of the universe and that God created the laws which govern the universe. However, they did not believe that God interfered in the natural world or daily lives of people, nor did they believe in miraculous events.
Which Enlightenment philosopher believed that human social advancement had come about and would continue to evolve as a result of science and reason?
Voltaire believed that scientific and rational advancements would eventually lead to a society free from nationalistic and religious prejudice.
Key Concepts: The Age of Enlightenment
The Enlightenment heralded a new willingness to question authority in all areas of life. Scientific discoveries increased rapidly, and the questioning of the monarchy led to political reform and revolution. In religion, skeptics increasingly challenged the authority of organized religion and attempted to find a basis for morality outside religion altogether.
The Enlightenment also saw the rise of deism, the belief that a God had created and designed the world but did not directly intervene in its affairs. This was also called the “watchmaker God,” a reference to a watchmaker’s role in creating a watch but relative neglect once it was completed and events are set into action.
The Enlightenment also saw the rise of deism, the belief that a God had created and designed the world but did not directly intervene in its affairs. This was also called the “watchmaker God,” a reference to a watchmaker’s role in creating a watch but relative neglect once it was completed and events are set into action.
Enlightenment thinkers were willing to challenge authority in all arenas of life. True or False?
True, Challenges to received wisdom resulted in rapid scientific advancement, and skepticism of organized religion allowed for the development of new moral systems. Political reform and revolutions followed the questioning of the monarch’s previously established “divine right” to rule.
Nature was treated with suspicion during the Enlightenment. True or False?
False, The suspicion of authority and reliance on human reason made nature a newly important realm. Scientists came to believe that they could best study God’s work through the observation and analysis of nature.
Religion of the Enlightenment
During the Enlightenment, there was a dramatic shift away from traditional Judeo-Christian religious thought.
Deists embraced religious authority from priests and kings. True or False?
False, Deists opposed both religious and political authority, both priests and kings, because they believed that each individual needed to be equally free to work out his or her own destiny.
Deists do not believe in divine intervention and therefore do not pray. True or False?
True, he deist God is a grand designer and creator, but he or she is not a close personal friend or consoler. Therefore, deists believe that ritual and ceremony are not logical and have no value.
Philosophy of the Enlightenment
During the Enlightenment, reason, rational thinking, and observation were key to uncovering philosophical truths. Enlightenment philosophers were concerned with abstract concepts pertaining to the social realm, such as justice, morality, law, government, and basic human rights. They developed their theories in conjunction with scientific theories and modes of thinking developed prior to and during this period. Three prominent philosophical movements during the Enlightenment were rationalism, empiricism, and skepticism.
René Descartes
was a French philosopher, writer, and mathematician. From his “first principle,” his Cogito ergo sum—”I think, therefore I am”—Descartes was able to deduce, at least to his own satisfaction, the existence of God, albeit a Deist God, neither interested in human affairs nor endowed with human character. Wrote Mediations on First Philosophy , in which the narrator meditates upon the nature of knowledge and human existentence.
Immanuel Kant
he cornerstone of his system of ethics is consistency. Absolute rules embody consistency. Kant believed that if we agree and apply the same principles to every applicable situation, we will have a coherent system of morality. Kant also argued that people needed to learn to think for themselves in order for societies to advance.
Mary Wollstonecraft
was an English writer, philosopher, and feminist who argued for the advancement of women, affirming that women were capable of rationality and that they should be educated.
John Locke
was one of the most influential philosophers and political theorists in British history. Many current ideas about selfhood, identity, and the way the mind works come from Locke. Locke also wrote highly influential books on government, providing a basis for the American political experiment. Published Two Tretises of Government.
–
–
The Social Contract Theory
Suggests that a formal society or state structure is born through an agreement, either conscious or subconscious, between individuals in which each relinquishes some of his or her individual rights for the sake of establishing a larger state with ultimate authority.
Thomas Hobbes
was an English philosopher whose work created a foundation for modern political science and philosophy. He is best known for his book Leviathan, which addressed the origin of states and governments and led to the development of the highly influential Social Contract Theory. also argued that the absence of absolute authority figure would lead to a “War of all against all”
Voltaire
was a writer and French philosopher who satirized self-proclaimed high-mindedness and rationality. He was skeptical of those who are too self-assured and those who are thoughtlessly cruel because of that assurance. His satire Candide attacks the Optimism of -Gottfried Leibniz, a philosophical stance predicated on the theological belief that all things, good or bad, happen for a reason.
The Encyclopédie
represented a fundamental principle of the Enlightenment: to accumulate, codify, and preserve human knowledge by providing rational information on important topics to the general public.
Denis Diderot
helped create the greatest encyclopedia in the 18th century with Jean le Rond D’alemert. He wrote philosophical dialogues that explored the theory and consequence of materialism: the idea that the universe is entirely composed of matter and without a God.
Jean-Jacques Rousseau
believed that the native peoples encountered through trade and colonization were, in some ways, morally superior, arguing that a person is at his or her best in wholly natural environments and is corrupted by the environments of society.
Rationalists
believed that human reason is the key to knowledge.
Empiricists
believed that all knowledge is derived through our senses and based on ideas and theories on testing, observation, and experience.
Skepticism
departed from both rationalism and empiricism in that it criticized our ability to perceive and understand the world around us, acknowledging the limitations of human reasoning.
categorical imperative
according to Kant, is an absolute and universal moral demand or obligation founded on reasoning. In a sense, it is a rule for making other rules (or what Kant calls maxims).
For Locke and the empiricists, moral behavior is based on ___________.
pleasure and pain, For Locke and the empiricists, moral behavior is based on pleasure (good) and pain (evil). We decide morality by our senses.
Which did Rousseau believe was an example of a barbaric practice justified by an over-rationalizing society?
slavery, Rousseau believed that the self is corrupted by more developed societies, which have lost the primal touch of prioritizing liberty; thus, they allow slavery.
The cornerstone of Kant’s system of ethics is __________.
consistency, For Kant, the cornerstone of his system of ethics is consistency. Kant believed that if we apply the same principles to every situation, we will have a coherent system of morality.
Voltaire…
agreed with Alexander Pope’s phrase, “presume not God to scan”, Voltaire believed, as Alexander Pope did, that expecting humans to scale the heights of wisdom and success is folly.
Skepticism:
The school of “rational skepticism” was prominent during the Enlightenment to ensure that philosophers reached conclusions based on reason, not prejudice.
Rationalism:
The philosophy of rationalism also put an emphasis on the role of reason as the key to knowledge.
Empiricism
First developed in the Renaissance by scientists such as Francis Bacon, empiricism may be defined as basing ideas and theories on the direct experience of the senses, including experimentation, as opposed to knowledge gained from books.
Logic:
The Enlightenment valued logical thinking, following formulas based on facts in order to arrive to a conclusion.
Progress:
The progress of human knowledge and society was an important goal for Enlightenment intellectuals.
Revolution:
Progress, emphasis on reason, and philosophical advancements led to political revolution throughout the Western world, especially in the American colonies and France.
Order:
Enlightenment thinkers and leaders sought to design political and social order that reflected natural laws and God’s will.
Clarity:
During this time, a system of philosophical clarity was also developed, largely by the mathematician Gottfried Leibniz.
Deism:
A shift in religious thinking also took place with the growth of deism, a belief system that credits God as the original architect of the universe’s natural laws but who does not currently oversee the events of the world.
Classicism:
In the arts, a resurgence of classical ideals like harmony, realism, and reason inspired the neoclassical movement.
Literature of the Enlightenment
Enlightenment literature was focused on rational prose and social reform.
Popular authors and works of the Enlightenment included:
-Jean-Jacques Rousseau, whose novel Emile uses logic and rational thought to address a new approach to education. This new model challenges social boundaries;
◦Samuel Richardson, whose novel Pamela challenges the boundaries of social status by evoking sympathy for a servant girl that tries to maintain her virtue;
◦and Alexander Pope, whose mock-epic poem “The Rape of the Lock” pokes fun at the upper class’ preoccupation with appearance rather than such virtues as humor and grace.
◦Samuel Richardson, whose novel Pamela challenges the boundaries of social status by evoking sympathy for a servant girl that tries to maintain her virtue;
◦and Alexander Pope, whose mock-epic poem “The Rape of the Lock” pokes fun at the upper class’ preoccupation with appearance rather than such virtues as humor and grace.
Jean Jacques Rousseau
Emile-
Theme-Rationalism, Logic, Progress.
Enlightenment techniques-uses reason in his social critique
In this work, what makes you free is to be unattached to what others tell you is reasonable and important.
•In this work, the main character comes to represent the writer’s ideal of a “natural” man
•This work addresses sound reason behind educational reform and education as a method of reforming social inequality.
Theme-Rationalism, Logic, Progress.
Enlightenment techniques-uses reason in his social critique
In this work, what makes you free is to be unattached to what others tell you is reasonable and important.
•In this work, the main character comes to represent the writer’s ideal of a “natural” man
•This work addresses sound reason behind educational reform and education as a method of reforming social inequality.
Samuel Richardson
Pamela-
Theme-Progress and Sympathy.
Enlightenment techniques-uses sensibility in his novel to provide a social critique.
this work, the main character works for a man who takes advantage of his class position over the main character.
•This work focuses on the ability of an individual to enact social change.
•This work addresses the limitations and dangers of the existing class systems.
Theme-Progress and Sympathy.
Enlightenment techniques-uses sensibility in his novel to provide a social critique.
this work, the main character works for a man who takes advantage of his class position over the main character.
•This work focuses on the ability of an individual to enact social change.
•This work addresses the limitations and dangers of the existing class systems.
Alexander Pope
The rape of the lock
Theme-Classicism, Progress, Order.
Enlightenment techniques-uses satire in his poem, written in heroic couplets, to provide a social critique.
This work gives a critique of the wealthy classes in England as lacking true values and focusing too heavily on vanity and frivolity.
•In this work, the main character is emotionally scarred by the actions of a Baron.
•The Enlightenment techniques used in this work were the use of writing in heroic couplets and the use of satire.
Theme-Classicism, Progress, Order.
Enlightenment techniques-uses satire in his poem, written in heroic couplets, to provide a social critique.
This work gives a critique of the wealthy classes in England as lacking true values and focusing too heavily on vanity and frivolity.
•In this work, the main character is emotionally scarred by the actions of a Baron.
•The Enlightenment techniques used in this work were the use of writing in heroic couplets and the use of satire.
Why was the novel an appropriate medium for conveying the theme of sympathy?
The novel’s length allowed for the development of complex characters and plots, evoking sympathy from readers as they became more and more invested.
How does the novel Pamela reflect period themes?
The novel challenges the boundaries of social class by showing that happiness is possible between a servant and her employer.
The novel evokes sympathy for the main character by threatening her virtue.
The novel appeals to the everyman by featuring the plight of a servant.
The novel evokes sympathy for the main character by threatening her virtue.
The novel appeals to the everyman by featuring the plight of a servant.
The phrase “a spoonful of sugar helps the medicine go down” means that medicine (which typically tastes bad) is easier to swallow when paired with something delicious. Similarly, things that are unpleasant are easier to accept if they are paired with something pleasant. Which Enlightenment work uses this strategy to convey its message?
“The Rape of the Lock” uses humor to soften the critique of the upper class’ focus on the conceits of appearance rather than “real” virtues, such as truth or reason.
Candide’s biggest struggle is with keeping his outlook on life _______.
Candide constantly struggles to remain optimistic
Voltaire was attacking the philosophers of the time with Candide. True or false?
True, Voltaire disagreed with the philosophy of optimism for optimism’s sake and set out to prove that the world was a dark and cruel place filled with dark and cruel people.
Which of the following religions does Jacques practice?
Jacques is an Anabaptist and therefore has never been baptized. He shows more “Christian kindness” to Candide than any of the Christians he has previously encountered.
Voltaire created the idea of publicly critiquing Christianity, and his book was banned for it. True or false?
False, Voltaire was not the first to publicly critique Christianity (or religion), but he popularized the practice, and his book was banned for it.
Neoclassical Theater
Neoclassical playwrights turned to subjects based on classical myths and adhered to classical unities of time, place, and action.
Moliere
Tartuffe-
Theme-Piety and Reason
Neoclassical techniques-uses satire to deliver his religious and social critique.
Theme-Piety and Reason
Neoclassical techniques-uses satire to deliver his religious and social critique.
Female actors performed in Neoclassical productions. True or False?
True
Neoclassical productions featured actors speaking naturally and wearing simple, realistic costumes. True or False?
False, Actors in Neoclassical productions spoke highly stylized language while wearing elaborate costumes.
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of the Neoclassical play Tartuffe?
It celebrates those who falsely convey a sense of religious piety. Tartuffe is a critique of false religious piety.
Neoclassical Art and Architecture
Neoclassicism was an 18th century art and architecture movement that looked to Greek and Roman art for models of harmony, idealized realism, and reason. It shunned the ostentatious elements of the Baroque and Rococo styles and promoted the themes of order, progress, and civic virtue
Johann Joachim Winckelmann
whose writings prompted the neoclassical movement;
Jacques-Louis David,
who painted scenes that emphasized civic virtue and civic morality; Oath of Horatii

Angelica Kauffmann
who was one of the most popular portraitists of her time

John Singleton Copley
who created portraits and history paintings; Portrait of Mr. and Mrs. Thomas Mifflin(1773) , Watson and the Shark

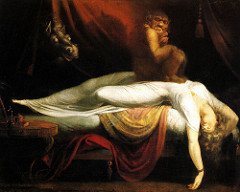
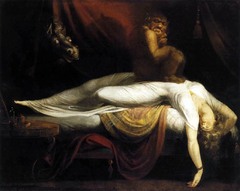
Henry Fuseli
whose paintings often explored elements of the supernatural, The nightmare
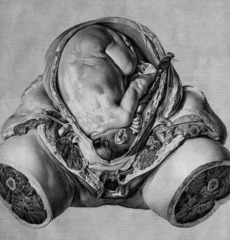
William Hunter and Jan van Rymsdyk
whose drawings contributed to the study of the female reproduction process. Child in Womb
Examples of Neoclassical architecture
include the Brandenburg Gate in Berlin, the Panthéon in Paris, and Monticello, Thomas Jefferson’s home in Virginia.

chiaroscuro
contrast of light and dark to achieve the illusion of depth

Classical Period art plays with intricate decorations and bright colors in order to convey opulence. True or False?
False, Classical Period art was a reaction to the ornate Rococo style of art in that it was simple and austere.
Which of the following Neoclassical paintings explored elements of the supernatural?
Henry Fuseli’s The Nightmare features elements of the supernatural, including a demon who sits on top of a sleeping woman and a horse lurking in the background.
Which of the following structures is NOT an example of Neoclassical architecture?
St. Paul’s Cathedral in London is an example of architecture from the Baroque Period.

According to Dr. Paula Carabell, what elements found in the painting Oath of the Horatii indicate that it is representative of the Neoclassical Period?
Neoclassicism pulled from Roman art and architecture, which, Dr. Carabell explains, is represented in the Roman arches of the painting. In addition, the anguished figures of the women reflect the notion that they are destined to lose their husbands, brothers, or sons to battle, as there was a prevailing notion that allegiance to country was more important than allegiance to family.

According to Dr. Paula Carabell, the painting The Death of Marat likens Marat to which historical figure?
In the painting, The Death of Marat, David depicts Marat’s lifeless body with its head leaned back and his arm forward—a posture that, at the time, was well-known to represent Christ.

Classical Music
The classical music genre refers to European music that was composed around 1730 to 1820. The music of this period embraced the Enlightenment focus on balance, order, and structural clarity. Composers heightened the contrast between musical lines and enjoyed a greater depth and variety in orchestral texture.
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart
who composed sonatas, symphonies, masses, concertos, and operas. Some of his most well-known works are Einekleine Nachtmusik, Symphony No. 40 in G minor, and the opera Le Nozze De Figaro (“The Marriage of Figaro”).
Joseph Haydn
another prominent classical composer with such works as Symphony No. 101 (“The Clock Symphony”).
Ludwig van Beethoven
started to compose music during this period and continued to create masterpieces during the subsequent Romantic Period. Two of his most famous symphonies are Symphony No. 5 in C minor and Symphony No. 9 in D minor.
Who commissioned the work Einekleine Nachtmusik?
One of the mysteries surrounding Mozart’s Einekleine Nachtmusik is the person or people who commissioned it.
Which of the following life stressors may have influenced the mood and tone of Mozart’s Symphony No. 40 in G minor?
Mozart’s wife’s ill health put a serious strain on him and, coupled with a decline in popularity and his father’s death, may have contributed to the dischordant, frantic tone of the piece.
If the musical notation staccato instructs the bassoons and flutes in “The Clock Symphony” to set a tone similar to the “tick-tock” of Big Ben, we can infer that staccato means…
The term staccato indicates that the notes should be short and separated, like the ticking of a clock.
Mozart’s Le Nozze De Figaro is a(n) _________________.
opera
Classical music is more focused on polyphony and ornamentation than music from the Baroque Period. True or False?
False. Classical music is more focused on balance, order, and structural clarity than the music from the Baroque Period. It features a more homophonic texture, which elevated shorter, more lyrical melodies over slower, more chordal harmonic progressions.
Cultural Exchange and Diversity in the Enlightenment
Cultural exchange and diversity were key aspects in the Enlightenment pursuit of reason and scientific thought and the suppression of traditional biases.
• The rise of capitalism facilitated the exchange of ideas and cultural practices, which intellectuals used in shaping their philosophies.
• Enlightenment thinking emphasized the role that individualized thought could play in crossing all racial and religious lines.
• Many Enlightenment thinkers rejected the tradition of slavery, looking to reason and individualized thought.
• Slave narratives were published during this time, enriching the Enlightenment philosophies with a new viewpoint and experience.
• The music of the time period was also diversified by the popularization of spirituals, or slave songs, which often featured religious themes and even hidden messages meant only for fellow slaves.
• The rise of capitalism facilitated the exchange of ideas and cultural practices, which intellectuals used in shaping their philosophies.
• Enlightenment thinking emphasized the role that individualized thought could play in crossing all racial and religious lines.
• Many Enlightenment thinkers rejected the tradition of slavery, looking to reason and individualized thought.
• Slave narratives were published during this time, enriching the Enlightenment philosophies with a new viewpoint and experience.
• The music of the time period was also diversified by the popularization of spirituals, or slave songs, which often featured religious themes and even hidden messages meant only for fellow slaves.
Which of the following is NOT true of spirituals, or slave songs?
using musical instruments, Spirituals were usually performed a cappella, or without instrumental accompaniment.
What philosophy was widely popular during the Enlightenment?
the concept that logic and reason could break down the established, rigid order and
the concept that dividing social boundaries could be breached by individual thought
the concept that dividing social boundaries could be breached by individual thought
Which statement summarizes a trend of the Enlightenment?
The diversity of information brought about higher thinking.
The Enlightenment’s Influences on Contemporary Life
The views of Enlightenment thinkers and writers have impacted our modern philosophy, particularly in the realm of politics.
•The modern emphasis on rights, knowledge and the betterment of mankind can be traced back to the Enlightenment.
•Jonathan Swift’s Gulliver’s Travels popularized political satire; it has continued to this day in the form of political cartoons and television shows that poke fun at various aspects of government.
•On Christmas Day 1989, American composer Leonard Bernstein conducted a performance of the fourth movement of Beethoven’s Symphony No.9 (the “Ode to Joy” movement) at the Brandenburg Gate. The performance celebrated the fall of the Berlin wall a few weeks earlier and featured singers from both West Germany and East Germany.
•The Enlightenment produced an imperialist mentality held by many western Europeans and their colonial offspring (like the United States). This “White Man’s Burden” has led many Westerners to believe it is their duty to “enlighten” the rest of the world.
•This sense of superiority is at the core of American exceptionalism, the belief that the United States is the greatest nation on earth and that it is the most advanced in terms of political development and individual freedom.
•The modern emphasis on rights, knowledge and the betterment of mankind can be traced back to the Enlightenment.
•Jonathan Swift’s Gulliver’s Travels popularized political satire; it has continued to this day in the form of political cartoons and television shows that poke fun at various aspects of government.
•On Christmas Day 1989, American composer Leonard Bernstein conducted a performance of the fourth movement of Beethoven’s Symphony No.9 (the “Ode to Joy” movement) at the Brandenburg Gate. The performance celebrated the fall of the Berlin wall a few weeks earlier and featured singers from both West Germany and East Germany.
•The Enlightenment produced an imperialist mentality held by many western Europeans and their colonial offspring (like the United States). This “White Man’s Burden” has led many Westerners to believe it is their duty to “enlighten” the rest of the world.
•This sense of superiority is at the core of American exceptionalism, the belief that the United States is the greatest nation on earth and that it is the most advanced in terms of political development and individual freedom.
Which Englightenment philosophy gave rise to such modern-day media as political cartoons?
Government exists to serve the governed
According to scholars, what was the cost of the political satire that came as a result of Enlightenment philosophy?
a loss of respect for authority
On Christmas Day 1989, American composer Leonard Bernstein conducted a performance at the Brandenburg Gate. He played “Ode to Joy;” however, he changed “joy” to ___________________.
Freedom
A person who subscribes to the notion of American exceptionalism would likely support U.S. intervention in countries that are struggling to establish a political structure.
American exceptionalism refers to the belief, held by many Americans, that the United States is the greatest nation on earth and that it is the most advanced in terms of political development and individual freedom.
Which of the following figures was an early feminist who argued that women should be educated?
Mary Wollstonecraft Her daughter Mary Wollstonecraft Godwin, later Mary Shelley, became the famous author of Frankenstein.
During the Age of Enlightenment, the questioning of a monarch’s _______ led to political reform and revolution.
divine right
The Neoclassical playwright ________ was best known for his plays Tartuffe and The Misanthrope
Jean Baptiste Molière
______ is the belief that God created the natural laws that govern nature but that he does not directly intervene or interfere in any way.
Deism
Immanuel Kant developed which ethical system?
Duty driven ethics
Which of the following figures was a Deist?
Thomas Jefferson
Kant believed that the cornerstone of a coherent system of morality was __________.
consistency
Which of the following Enlightenment writers wrote an article for Diderot’s Encyclopédie about the Social Contract?
Rousseau
Which of the following works comments on the rising skepticism of religion during the Enlightenment Period?
Candide by Voltaire
The columns of the Brandenburg Gate in Berlin feature which Greek architectural style?
Doric
Poet Alexander Pope uses __________ in his poem “The Rape of the Lock” to critique 18th century high society and its focus on vanity.
Satire
This school of Enlightenment philosophy acknowledged the limitations of human reasoning
Skepticism
Why was John Singleton Copley’s portrait of Mr. and Mrs. Thomas Mifflin unlike typical portraits of the day?
Copley portrayed Mrs. Mifflin, Sarah (Morris), as a key figure in the relationship. She is placed in front of her husband and posed to meet the viewer.

Which of the following was a practice in Neoclassical theater that allowed playwrights to focus on the tragic interplay between men and women?
Female actors,
Watson and the Shark (1778) by John Singleton Copley

The Death of General Wolfe (1770) by Benjamin West

Nicolas-Sébastien Adam’s mythical Prometheus

Psyche Revived by Cupid’s Kiss (1787) by Antonio Canova

The Grand Odalisque (1814) by Jean Auguste Dominique Ingres

Disciplines such
as natural history, modern science, and natural law were all born out of the Enlightenment.
Ideas such
as the separation of church and state, religious tolerance, and free speech were also fruits of the Enlightenment.
Thomas Jefferson
drafted both and The Statute of Virginia for Religious Freedom. He served as the third President of the United States and founded the University of Virginia. The Declaration of Independence captures in a succinct and powerful way the relationship among humanism, Enlightenment philosophy, and political governance.
The Declaration of Independence established the
idea of a new nation that was a product of the philosophies of the era, and it influenced more than just a collection of British colonies. The view expressed within its words firmly asserted the ideas of individual rights and helped to establish the sense of individualism that so governs the modern United States and many other European nations.
Many intellectual philosophes,
inspired by scientific discoveries in physics and biology, preferred deism, a belief system that credits God as the world’s creator, who established the natural law and order but who otherwise does not interfere with humanity.
The philosophes
embraced deism largely because it was a concept that appealed to the rational mind. Deism rejected the details of Christianity and believed in a deity who ordained the order in the universe and let that order operate.
Deists did not
practice worship or ritual, since they did not believe in divine intervention, but instead strove to understand the order that God put into place.
Whether the Enlightenment produced the novel,
a longer form of prose that allowed for more complex plot and character development, or expanded upon it, the genre was a perfect vehicle for the period theme of sympathy, since authors had the literal space to develop characters richly and to devise intricate plots.
Enlightenment literature often
blended real life with philosophical or ethical reflection, making biographies, essays, and travel narratives very popular.
The printing press popularized literature and made it available to people of all social classes.
For this reason, tone was geared toward the newly literate, whose intellectual appetites were fed in public meeting places like the cafe.
Everything from
the wardrobe to the motions and gestures of the characters on the stage characterized Neoclassical theater’s grandiosity and opulence.
Neoclassical theater featured either
“the heroic tragedy” or “the comedy of manners,” as tragedy and comedy were not mixed.
The use of female actors in Neoclassical plays
was a new convention in England that allowed playwrights to focus on the tragic interplay between men and women.
Three of the leading Neoclassical playwrights were
from France: Jean Batiste Moliére, Jean Racine, and Pierre Corneille.
In his comedy Tartuffe,
Moliére uses satire to critique false religious piety and to highlight the contrasts between irrationality and reason.
WGU C100 CH 6 NeoClassical Period. (2019, Feb 12). Retrieved from https://paperap.com/wgu-c100-ch-6-neoclassical-period/

